In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, automating accounts payable processes using software has become a game-changer for organizations seeking to enhance efficiency and reduce manual errors. Whether undergoing a financial transformation or revamping accounts payable processes for the first time, choosing the right software solution is crucial. Companies need to have a firm understanding of the top accounts payable software features that ERPs require to maximize productivity. For instance, one fundamental decision to make is whether to adopt a centralized or decentralized accounting approach.
This blog delves into the key features companies should consider when selecting an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system to streamline and automate these critical financial operations. By harnessing accounts payable automation, companies unlock significant time and cost savings, improve accuracy, and gain valuable insights for strategic decision-making.

One of the critical aspects of automating accounts payable processes is ensuring that month-end are centralized across all entities, eliminating the need for manual consolidation and the time-consuming task of chasing paper from various subsidiaries or other branches. Centralized payment processing software provides a significant advantage by allowing companies to streamline intercompany accounting and automate the transfer of critical information such as invoicing records in a timely manner. Centralization reduces the time and effort spent processing month-ends for multiple entities within an organization.
To illustrate the tangible benefits of such a system, let’s consider the example of American Software, a company that successfully centralized accounting processes. In their first year, they managed to save a remarkable $50,000 in operational costs. By eliminating the need for separate checks for each entity and streamlining intercompany transactions, American Software significantly reduced the time spent on manual processes, enhanced efficiency, and achieved substantial cost savings. This example highlights the potential savings and efficiency gains that can be achieved by implementing a centralized system. By reducing manual efforts, organizations can allocate their resources effectively, focus on strategic initiatives, and drive business growth.
Security features can seem like a vague concept if you’re not sure what to ask about. To ensure that the necessary safety measures are being taken to protect customers and financial data, companies can consult with software providers before investing to see what sorts of protocol are in place. Companies should gain a clear understanding of the security features and protocols in place before investing in any software.
It’s wise to inquire about the specific encryption methods used, the presence of firewalls and intrusion detection systems, and seek information about multi-factor authentication options. Software providers can also provide insights into the regularity and comprehensiveness of security audits, vulnerability assessments, and employee training programs. Through this collaboration, companies can verify that the robust safety features they require are indeed implemented and aligned with their security needs, ensuring enhanced protection for sensitive financial data and customer information.
Recommended reading: 5 steps to reduce and assess security risk in mergers and acquisitions
Full integration of accounts payable software with your other financial systems and existing software is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, when all systems seamlessly integrate, there is no need for complex data transfers or extensive configuration processes, leading to a smoother and more efficient implementation. This saves valuable time and resources for the company, allowing them to focus on their core operations.
Integrated accounts payable software also cuts down on training requirements. When the software integrates seamlessly with existing financial systems, employees can leverage their existing knowledge and skills. They do not have to undergo extensive training on a completely new system, reducing the learning curve and accelerating the adoption process. This ensures a more seamless transition and minimizes disruptions to daily operations.
Moreover, the integration of accounts payable software enables a seamless flow of information across different financial systems. Data can be automatically synced and shared between systems, eliminating the need for manual data entry or transfers. This not only saves time but also reduces the risk of introducing errors that can occur when manually transferring data.
An example of the benefits of full integration can be seen in the case of Northern BI. By investing in a system that allowed them to migrate from on-premise accounting with Dynamics GP to Dynamics 365 BC. They were able to reduce their billing workload by 50%. This highlights how seamless integration eliminates the need to learn an entirely new system from scratch, enabling businesses to quickly leverage the benefits of the new software and realize significant efficiency gains.
Automated invoice processing and approval workflows are critical features that enhance the efficiency and accuracy of accounts payable software. Manual invoice processing is often plagued with challenges such as time-consuming data entry, manual routing for approvals, and the potential for errors. By automating these processes, companies can streamline their accounts payable operations and mitigate the risks associated with manual handling.
With automated invoice processing, invoices can be electronically captured and entered into the system, eliminating the need for manual data entry. This reduces the likelihood of errors and speeds up the invoice processing timeline. Additionally, automated approval workflows ensure that invoices move seamlessly through the necessary channels for review and approval. Instead of relying on manual routing and physical paperwork, the software can automatically route invoices to the appropriate individuals based on predefined rules and hierarchies. This not only accelerates the approval process but also provides visibility into the status of invoices at any given time.
Real-time visibility into payment status and transaction history is a valuable feature that empowers businesses to make informed financial decisions and proactively address any payment-related issues. With this feature, companies can access up-to-date information on the status of their payments, including whether invoices have been received, processed, approved, and paid. This real-time insight allows businesses to have a clear understanding of their cash flow and financial obligations, enabling them to plan and allocate resources effectively.
Furthermore, having access to real-time transaction history provides a comprehensive view of past payment activities. Companies can easily track and monitor their payment records, including details such as payment dates, amounts, and recipient information. This historical data can be vital for financial analysis, audits, and reconciliations, as well as for building strong relationships with suppliers or vendors.
The ability to view payment status and transaction history in real-time brings several benefits. It allows businesses to identify any potential payment delays or discrepancies promptly, enabling them to take immediate action to resolve issues. This feature also fosters transparency and accountability, as all stakeholders involved in the payment process can easily track and verify transaction details. Check out the core benefits of financial transformation for more information on the strategic advantage these insights give companies.
The ability to set and enforce financial policies and procedures is a critical feature of accounts payable solutions. It enables businesses to establish and maintain standardized practices that align with their financial governance requirements. By leveraging this feature, companies can define and enforce specific policies and procedures across all entities, ensuring consistent adherence to regulatory guidelines and internal controls.
Setting financial policies and procedures provides clarity and guidance to employees involved in the accounts payable process. It establishes a framework for handling financial transactions, expense reporting, vendor management, and other relevant activities. With well-defined policies in place, employees are equipped with clear instructions on how to process invoices, authorize payments, and handle exceptions, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring compliance with established protocols.
Advanced reporting and analytics empower businesses to gain deep insights into their financial operations and make data-driven decisions. With customizable dashboards and real-time data analysis, companies can access comprehensive and up-to-date information about their accounts payable processes. The ability to customize dashboards allows users to configure visual representations of key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics that are most relevant to their business. This provides a holistic view of accounts payable activities, including invoice processing time, payment cycle, vendor performance, and cash flow analysis. By having these visual representations at their fingertips, businesses can quickly identify trends, spot bottlenecks, and identify areas for improvement.
Real-time data analysis takes reporting a step further by providing instant access to live data. This enables businesses to monitor accounts payable performance in real-time and promptly address any issues that may arise. It also facilitates timely decision-making, as companies can proactively respond to changing financial circumstances or market dynamics. Companies can generate detailed reports and extract valuable insights from their accounts payable data. These insights can help identify cost-saving opportunities, optimize payment processes, negotiate better terms with suppliers, and enhance overall financial performance.
Scalability is a crucial feature that organizations should seek in an accounts payable solution. As businesses grow and expand, the volume of transactions and entities involved in the accounts payable process increases significantly. It is essential that the chosen solution can scale seamlessly to handle this growth without any compromise on performance or security.
A scalable accounts payable solution can efficiently manage the increased workload, ensuring that transaction processing remains swift and responsive. It should be capable of handling a higher number of invoices, payments, and vendors without experiencing performance bottlenecks. This scalability is essential to maintain operational efficiency and prevent any disruptions or delays in the accounts payable process.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance, a leading enterprise resource planning (ERP) solution, is undergoing a significant enhancement as it deprecates the Revenue Recognition functionality and introduces Subscription Billing as an improved alternative. This strategic move aims to provide customers with enhanced capabilities in managing subscription-based revenue and billing, ensuring seamless operations in modern finance environments.
April Olson, Head of Product at Dynamics 365 Finance, expressed her confidence in the collaborative efforts with Binary Stream, stating, “Because of their alignment with Microsoft, Binary Stream makes working together feel effortless. Not only do they support Dynamics 365 Finance with innovative solutions, but their growth mindset means they empower our customers with highly scalable solutions for modern finance that can handle the complexity of XaaS billing.”
Since April 2023, Revenue Recognition functionality no longer receives support for bug fixes. Customers are encouraged to adopt the improved functionality, Subscription Billing, as the primary revenue management solution. By October 2023, the Revenue Recognition feature will be entirely discontinued, and customers will be required to transition to Subscription Billing.
Subscription Billing introduces a comprehensive set of features that enable organizations to efficiently manage subscription revenue opportunities and recurring billing through flexible billing schedules. This enhanced functionality supports complex pricing and billing models, as well as revenue allocation at the line level. Furthermore, the solution ensures compliance with International Accounting Standards IFRS 15 and ASC 606 through multi-element revenue allocation.
The improved functionality comprises three modules that can be used independently or in combination, providing customers with a tailored experience for recurring contract billing, revenue and expense deferrals, and multiple element revenue allocation.
To support customers throughout the transition, Binary Stream, a trusted partner with over 15 years of expertise, will be available to provide guidance and support to teams managing the migration process.
Lak Chahal, CEO of Binary Stream, expressed enthusiasm about empowering customers on their subscription management journey, saying, “Our expertise in subscription management and commitment to customer success ensure that organizations can maximize the value of Dynamics 365 Finance and efficiently navigate the complexities of subscription-based revenue management.”
For more information on Subscription Billing and its features, please visit the Subscription Billing Overview on Microsoft Learn or if you’d like to find out about our comprehensive migration services, you can click here.
Finding innovative ways to improve the recurring billing and payments process should be at the core of any subscription billing strategy. Although what that means can be different depending on the industry or offering, there’s a need for most teams to streamline and automate critical components of revenue recognition and deferral workflows so that they can do more with less.
Modern billing doesn’t have to be complicated, yet many make it so. Rather than invest in the automation needed to bolster billing operations for strategic pricing strategies, they scramble to make month-ends, often resulting in high subscriber churn.
When you struggle to bill effectively, it impacts every level of your organization. With the rise of subscription options across industries, many need help to keep up with the flood of administrative work in finance departments.
If you want to meet customer demand and relieve your finance team of unnecessary work, you’ve come to the right place. This guide is your guide to improving your billing one step at a time.
Here’s what you’ll find inside your copy of the guide
Download your copy of the guide now by clicking this link.
As a customer base grows, subscription billing processes can make or break the average finance team—previously manageable workloads can quickly spiral out of control. Given the subscription economy’s growth, many accountants struggle to handle floods of new accounts, recognize revenue appropriately and produce accurate, timely invoicing. Teams often launch SaaS pricing models without first putting the financial tools and processes critical for efficient billing in place. In short, few undergo the financial transformation that subscription billing requires.
With so many moving parts to consider, accounts teams soon become swamped by the administrative burden of accelerated growth. Many of the tactics used in popular pricing strategies can lead to an unprecedented influx of new subscribers. For instance, limited free trials can cause administrative hiccups when teams need to upgrade to billing once the special offer is over. If only ten users subscribe, this is relatively easy, but if the campaign is successful, this might mean hundreds or even thousands of new accounts require updating. Companies will struggle to retain even the happiest subscribers if the transition to billing is not efficient and reliable.
Billing is at the heart of any good subscription pricing strategy, and several core processes are critical for success. The average customer expects a lot of autonomy when managing payments. Below is a list of some of the common expectations.
What customers expect from your billing processes:
Though the anatomy of the ideal subscription billing process can vary from company to company, there are universal best practices and considerations. This blog breaks down the core elements that successful processes have in common.
This statement may bring out the contrarian in some, others may feel personally attacked, and thoughts may run through the mind such as we’ve always managed it that way before, and of course, we can scale! These are all understandable attitudes toward the constant call for automation. But the truth is that manual billing is not tenable for building a healthy subscriber base.
There are often more time-draining activities in processes than teams think, and they add up. Finance teams need to assess manual tasks, which, if eliminated, could save them time every month. Many billing tasks can be automated, and creating a custom ERP checklist that includes those manual tasks, which are the most time-consuming, will be a decisive step forward for overwhelmed teams.
Ask lots of questions of your team. Do you input data manually? Do even minor updates lead to someone having to adjust each account manually? Is revenue recognized automatically? Are there lots of errors in your system, and why? By closely examining the problems that commonly arise, you can easily trace where the bottlenecks or issues originate. These pain points are the perfect place to begin the automation process.
One of the significant process changes with subscription billing management is that the sales and accounts team should only sometimes need to set up new customers. Most people are now used to subscribing and managing billing in contactless environments, where they feel in control of their usage and the platform. Although with more complicated products where it’s impossible to display custom pricing, there may be other options.
Still, with more straightforward offerings, it’s wise to empower subscribers to sign up without worrying about talking to someone on your team. A registration page that links to common FAQs, displays pricing and information in conversion-friendly copy, and walks the customer through each step, is the ideal way to sign up more subscribers without adding to the team’s workload. Enabling sign-ups frees the accounts team to focus on critical billing strategy rather than troubleshooting.
Sign-up billing process should include:
Usually, with subscription billing, customers can sign up at any time and choose various payment frequencies and tiers. The more complex the pricing options, the harder it can be to manage. If your team is responsible for scheduling and tracking invoices and payments over the phone or email, they will quickly become overwhelmed when your services get popular.
Payment gateways are the perfect solution to this challenge. The majority of your customers will be able to log in and manage their payments. Not only this, but the best recurring billing software will integrate with a payment gateway, often expanding the number of payment options you can accept. These gateways are significant as the customer base grows, allowing you to handle more complex customer issues and let customers take care of standard billing procedures such as updating credit card details and activating payments in a secure environment.
Subscription billing presents the challenge of proving compliance with accounting standards such as ASC 606 and IFRS 15. Those still implementing manual processes will need help to produce error-fee audit trails and may spend a significant amount of their labour simply combing through data to fix mistakes—time better spent on strategic initiatives.
Accuracy is vital to proving compliance. With the right solution, automation is possible, and companies can keep up. Just think, competitors may already be investing in better billing processes saving themselves valuable time and money. This global movement leaves only one question for today’s finance leaders: why not free up critical budget and personnel with automation, so you can reallocate resources and drive strategy?
It’s worth calculating the time your accounts team sinks into collections, revenue recognition and dunning for subscription billing. Once you’ve got this information, it will be easy to establish an ROI on recurring billing software.
The three key subscription billing processes to automate
There can be a steep learning curve for teams transitioning to subscription billing. If your accounts team has spent most of their careers managing manual, traditional billing, they may need to gain the expertise to handle complications presented by newer pricing strategies.
These teams may be the most reluctant to change the way they do business simply because they need the training to feel comfortable with the new processes. That’s why financial transformations and SaaS migrations require training, education and communication. Your team will need dedicated time to upskill to meet the demands of handling the growth in recurring billing accounts and experts to call on to ask those tricky accounting questions.
The nuances presented by advanced subscriber management mean that processes should be put in place so that even your most senior accountants can ask questions and discover practical ways to streamline billing. Invest in hiring a specialized expert on contract, or if you intend to invest in software, look for teams that offer a high degree of customer care, support and training.
How are you storing billing information? What systems are in place to protect your customers from data breaches or attacks? Security is so important in the billing world that it needs consideration at every step. Even if this isn’t top of mind for you, it will be for your subscribers, who will likely look for safe, encrypted environments. Manual invoicing can be a red flag to those used to more robust billing solutions where their information is stored safely and securely by familiar payment partners through a gateway. Check out this blog on the security features to look for in your payment gateway.
One of the failures of most overwhelmed accounting teams is the need for more reliable customer communication. Customers want to know when changes are being made to their billing, when a payment has failed, or if a free-trial or special offer is about to end. Erring on the side of over-communicating is preferable when it comes to matters of payment.
Often teams are so consumed with rolling out updates across relevant accounts that the communication piece becomes haphazard and inconsistent. With robust software, it’s possible to automate notifications (for instance, a new billing cycle, a failed payment, etc.) and roll out bulk updates—giving teams plenty of time to consider the strategy for best-communicating changes.
Critical pieces of communication around billing
As SaaS continues to rise in popularity and recurring billing models move from niche to normal, many businesses are migrating to modern pricing models and finding ways to expand their billing options. This transition often involves implementing new subscription billing processes and may even require the adoption of new solutions to help manage more demanding workflows.
Automated recurring billing software is a fantastic tool that will help position your finance team to handle the back end of rigorous expansion while keeping overhead to a minimum. Let’s explore seven ways recurring billing automation saves your company time and money.
Subscription pricing models and recurring billing options are incredibly agile, variable, and customizable. These advantages allow businesses to thrive in a fast-paced market but can increase the workload for your finance team. Accounting needs to be primed for the intense workload with an investment in automation. Invoicing is no longer straightforward—variable amounts, tiered pricing, and multiple billing frequencies are common factors that can quickly complicate your billing system.
Recurring billing automation is vital to achieving rigorous expansion and optimizing your recurring payment management. Spreadsheets won’t cut it when your finance department needs to process thousands of invoices each month. Augmenting human productivity with software automation to handle routine accounting processes allows your team to comfortably manage an expanding customer base without missing critical deadlines or making costly mistakes.
Leadership requires access to timely reports to act on financial insights and sustain a high degree of business agility. Therefore, accounting teams must achieve faster closes during period-ends. Automated recurring billing software accelerates these processes, and some solutions are built with real-time reporting, empowering team members to access performance insights from a single source of truth.
Real-time reporting was a critical value-add for OTC Markets Group. The business relied on a complex jigsaw of three decentralized systems that confused external auditors and potential shareholders. After implementing an automated recurring billing solution, they’ve reduced the time spent compiling month-end financial statements by 50%, saving over 120 hours of work per month. To read more about how OTC Markets Group minimized time spent on month ends, download the case study here.
Businesses dependent on manual data entry tend to suffer from unclear, messy, and error-riddled data, resulting in poor financial visibility. Gartner found that poor data quality costs companies $12.9 million annually on average. Yet, while teams sacrifice many hours entering information into systems, they often spend even longer fixing mistakes. Research has shown that 40% of workers spend up to a quarter of their week on manual data entry and related repetitive tasks.
QTS Data Centers (QTS) struggled to scale their operations appropriately due to a significant number of core processes being redundant and time-consuming. Prior to implementing automated recurring billing, they operated 33 separate databases across multiple entities and manually processed 38,000 unrecognized deferral entries. The new software automated recurring billing activities across all entities, accounting for a 30% reduction in redundant processes and saving 11 days on end-of-month close cycles. To read more about how QTS regained control over their data management systems, download the case study here.
Automated recurring billing software streamlines workflows, liberating teams from obsolete, repetitive tasks and minimizing clerical errors. Real-time reporting and historical invoicing empower leadership with contextualized insights based on the most up-to-date information at any given time. The software also makes it simpler for finance teams to maintain best practices in data management and uphold the seven standards of reliable data.

Mistakes can cost your team hours, if not days, of extra work. These losses quickly add up, resulting in entire weeks lost to checking and correcting errors in the system. Missing a critical deadline, billing the wrong amount, invoicing the wrong customer—these are all examples of errors that contribute to customer churn. According to a recent study by PWC, 32% of all customers surveyed reported they would stop doing business with a brand they loved after one bad experience.
Automated recurring billing saves your business from these unnecessary blunders, helping maintain a loyal base of happy recurring customers and improving cash flow. For example, Sunshine 811 lacked complete visibility of their billing processes and, due to an immense amount of labour-intensive administrative work, frequently sent out invoices that were inaccurate and/or late.
By adopting automated recurring billing software, they recouped $15,000 annually and now accurately bill over a thousand members each month. For the complete story of how Sunshine 811 took back control over their billing system, download the case study here.
Subscriber churn is one of the costliest challenges that subscription businesses face. Subscription services lose approximately 2% of customers monthly due to expired credit cards, and failed payments account for $278 million in lost revenue for the subscription industry over the past twelve months.
Companies stand to regain a huge chunk of their monthly recurring revenue (MRR) by communicating with their customers and implementing modern dunning processes. An automated recurring billing solution will enable you to master dunning and collections management to prevent subscription revenue leakage by automating credit card updates, dunning emails, and collection re-attempts. Your accounts receivable (AR) team will also recoup time to follow up with high-priority customers who need a more human touch.

Calculating taxes can quickly become overwhelming, particularly when companies expand operations into various regions. Managing multiple currencies and languages while complying with local tax requirements can take up a lot of resources, ultimately getting in the way of company growth targets.
Recurring billing automation saves time for your finance team when overseeing complex taxation requirements—instantly applying changes based on taxability rates and rules and accounting for exceptions. Depending on the software, your team can even automate other redundant or repetitive tax-related tasks, accelerating reporting for month-ends.
MoxiWorks was able to save 80 days annually by automating their recurring billing processes. The real estate software provider employed a team of 150 employees to manage over 340,000 active users, totalling $150 million annual recurring revenue (ARR). After implementing an automated recurring billing solution, they now save 15 days preparing taxes per year. To read more about how MoxiWorks cut down time spent on month ends, download the case study here.
ASC 606 and IFRS 15 protocols require companies to recognize revenue as they fulfil performance obligations, like delivering goods or services, rather than at the initial time of sale. However, it’s nearly impossible to manually track deferred revenue, especially when deferrals span many months and are distributed unevenly.
An automated recurring billing solution helps to organize your ledgers, maintaining tidy and accurate records that are audit-ready year-round. This saves your company from fines and penalties for non-compliance, as well as frees up your finance team to focus on more strategic tasks.
BT Conferencing greatly benefitted from adopting automated recurring billing software and now effortlessly manages 10,000 deferral accounts. The business struggled to keep up with rigorous requirements imposed by their parent company’s overall financial compliance team. However, the new solution reduced the labour required to complete month-ends to just 10% of one full-time employee’s workload. To read more about how BT Conferencing converted days’ worth of effort into the click of a button, download the case study here.
Advanced Subscription Management is a recurring billing solution that leverages automation to streamline workflows, support complex pricing models, and maintain compliance with international accounting standards. Fully embedded within Dynamics 365 Business Central, Finance, and Dynamics GP, you can accelerate your business’ agility and start saving. If you have any further questions or would like to book a demo with our experts, feel free to contact us anytime.
Payment gateways are an essential tool for processing e-commerce transactions securely. That’s why you need to understand how they work and what sets the best ones apart from the glut of options on the market. As businesses undergo exponential growth, many finance teams require help to manage the sheer volume of invoices. Without a solution to augment their productivity, bottlenecks form and errors creep in, damaging overall efficiency and leading to customer churn.
Empowering your customers to take ownership of their payment details allows them to play an active role in transactions. This takes some of the heat off accountants and enables them to focus on more strategic roles while building customer trust. Payment gateways also provide an extra layer of data protection, establishing a secure environment to process payments without compromising customer experience.
If you’re interested in a specific question about payment gateways, skip ahead by clicking on the topic below.
A payment gateway is an online payment solution that verifies credit card details and transfers funds for e-commerce transactions. It acts as an intermediary between the customer and the merchant, creating a secure environment to send and receive payment details between the merchant’s website, the customer’s financial institution, and the merchant’s financial institution.
There are three types of payment gateways:
1.) Redirect
2.) On-site
3.) On-site checkout and off-site payment
Redirect, or hosted, payment gateways forward the customer to a different website to complete their purchase. Therefore, the payment gateway does not integrate into the merchant’s website, which can result in fewer conversions.
On-site payment gateways mean the merchant’s server completes the payment process. Large enterprises typically implement these because they offer maximal control over the process and have the resources to manage higher complexity and responsibility.
Finally, some payment gateways offer a hybrid approach where the customer completes checkout on the merchant’s website, but a third-party redirect website processes the payment. This type of gateway is convenient and straightforward, like redirect gateways, but lacks the total control offered by on-site gateways.
A registered merchant account is a type of bank account required of all businesses to accept debit or credit cards and receive payment. Payment service providers typically provide these accounts for merchants.
A payment service provider (PSP) is a third-party company that offers payment services, including payment gateways. These businesses allow companies to accept online payment methods and remain compliant with industry security standards. You’ve probably already heard of some prominent companies, like PayPal or Stripe. SK Global Software offers a premier add-on solution facilitating payments through Microsoft Dynamics 365.
A payment portal refers to the front-end technology that collects customer payment information. Some common types of payment portals include:
A payment gateway will transfer data retrieved from the payment portal during a transaction.
A payment processor transfers a customer’s credit card information between the merchant’s point-of-sale system and the customer’s card network or bank. A payment gateway will request authorization of sensitive information from a payment processor during a transaction.
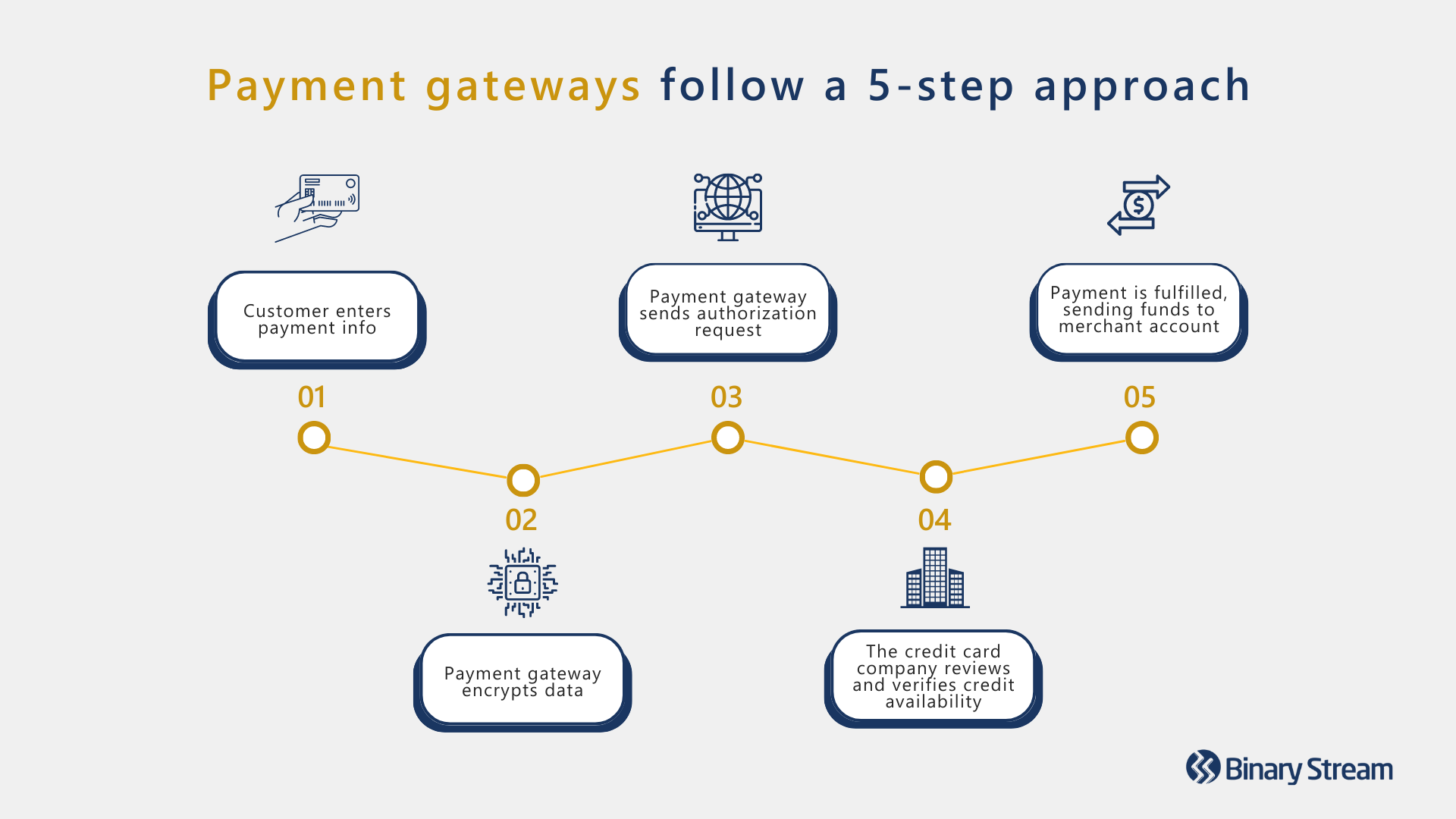
Payment gateways process transactions by following a five-step approach:
1.) The customer enters their payment information on the payment portal.
2.) The payment gateway encrypts their payment details and secures the connection between the portal, gateway, and processor.
3.) The payment gateway sends a transaction authorization request to the payment processor.
4.) The credit card company reviews and verifies credit availability. If sufficient funds exist, the payment processor authorizes the transaction request.
5.) Once the payment gateway receives authorization, the payment can be fulfilled, transferring funds to the merchant account.
Failed online payments are an unfortunate but relatively common occurrence. FlexPay research revealed that nearly half of all subscriber churn is due to failed payments. Therefore, make sure to carefully read the agreement with your provider, as it will include several warranties for the merchant (and sometimes the customer!), as well as a detailed breakdown of the liability of the payment gateway.
Depending on the agreement, PSPs may assume partial to full responsibility for failed transactions, owing the merchant compensation for financial damage. Nevertheless, PSPs are not liable for damages caused by third-party services.
In the event of a failed payment best practice is to directly communicate the error to the customer, then follow up with dunning email automation and payment retry cycles.
The three most common reasons payments fail include system downtime, payment technology errors, and compromised security. However, the transaction can also be unsuccessful because,
Some payment gateways route transactions to multiple payment processors to avoid these issues. With more options available, the system can attempt to resolve errors and downtime before sending the customer a failed payment notification.
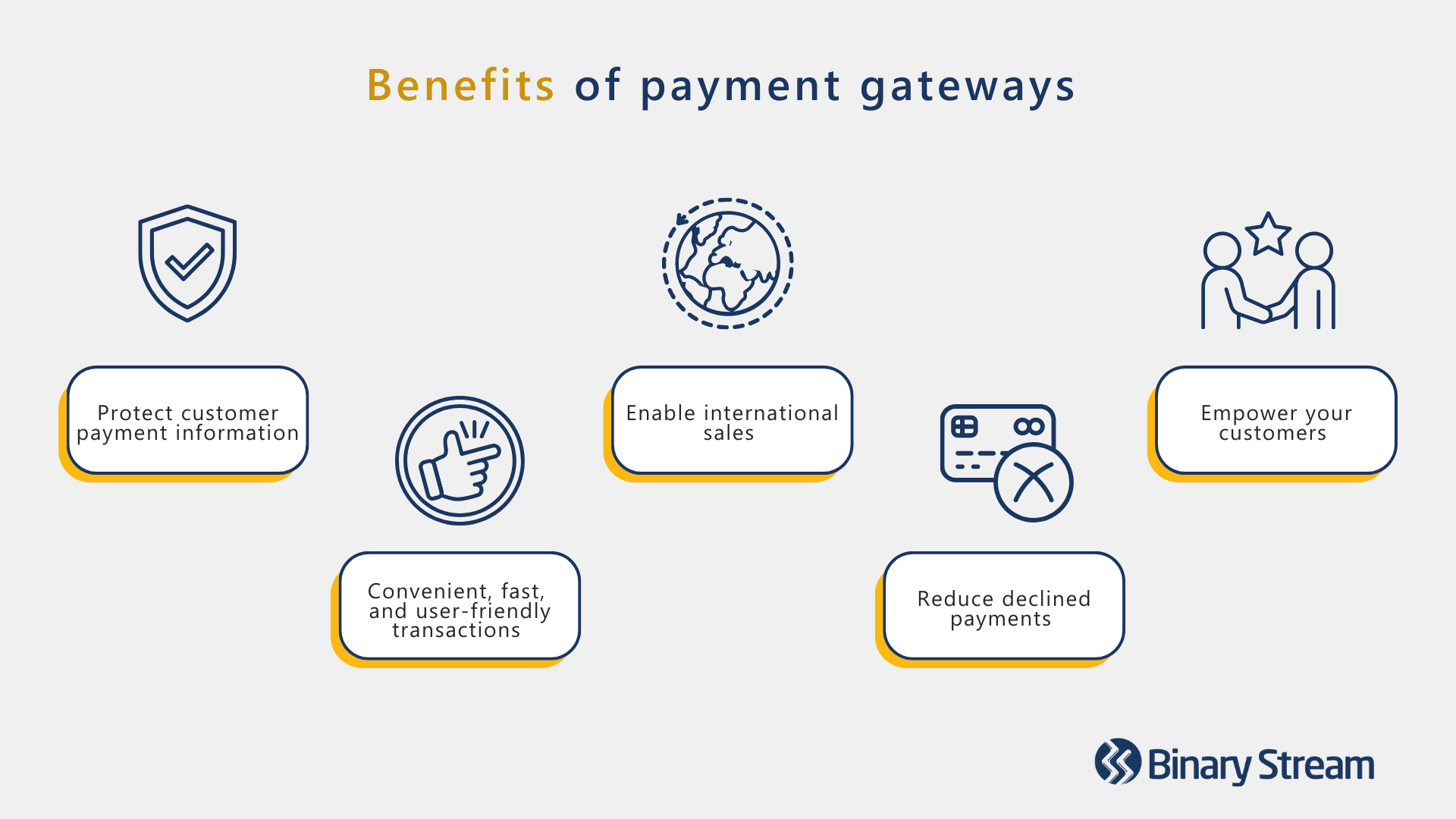
Payment gateways are the perfect tool to help manage e-commerce transactions and receive payments online. While finance teams might keep up with a reasonable number of monthly payments, it’s common for workloads to spiral out of control as your customer base expands.
The right payment gateway seamlessly fits into your everyday business operations to support exponential growth while protecting brand reputation and revenue. Modern customers crave convenience and a user-friendly payment process that they can trust. Empowering them to take an active role will build their confidence in online purchases with your company.
If you want more information, check out this blog for an in-depth look at five of the biggest benefits of payment gateways.
Providing a secure shopping experience is a non-negotiable component of successful e-commerce. Breaches could endanger your brand’s reputation and lead to costly fees. PSPs can fine companies $5,000–$100,000 monthly for non-compliance with the PCI DSS.
That’s why it’s vital to maximize the tools and protocols in place that are safeguarding customer information. Below lists five must-have security features for your payment gateway:
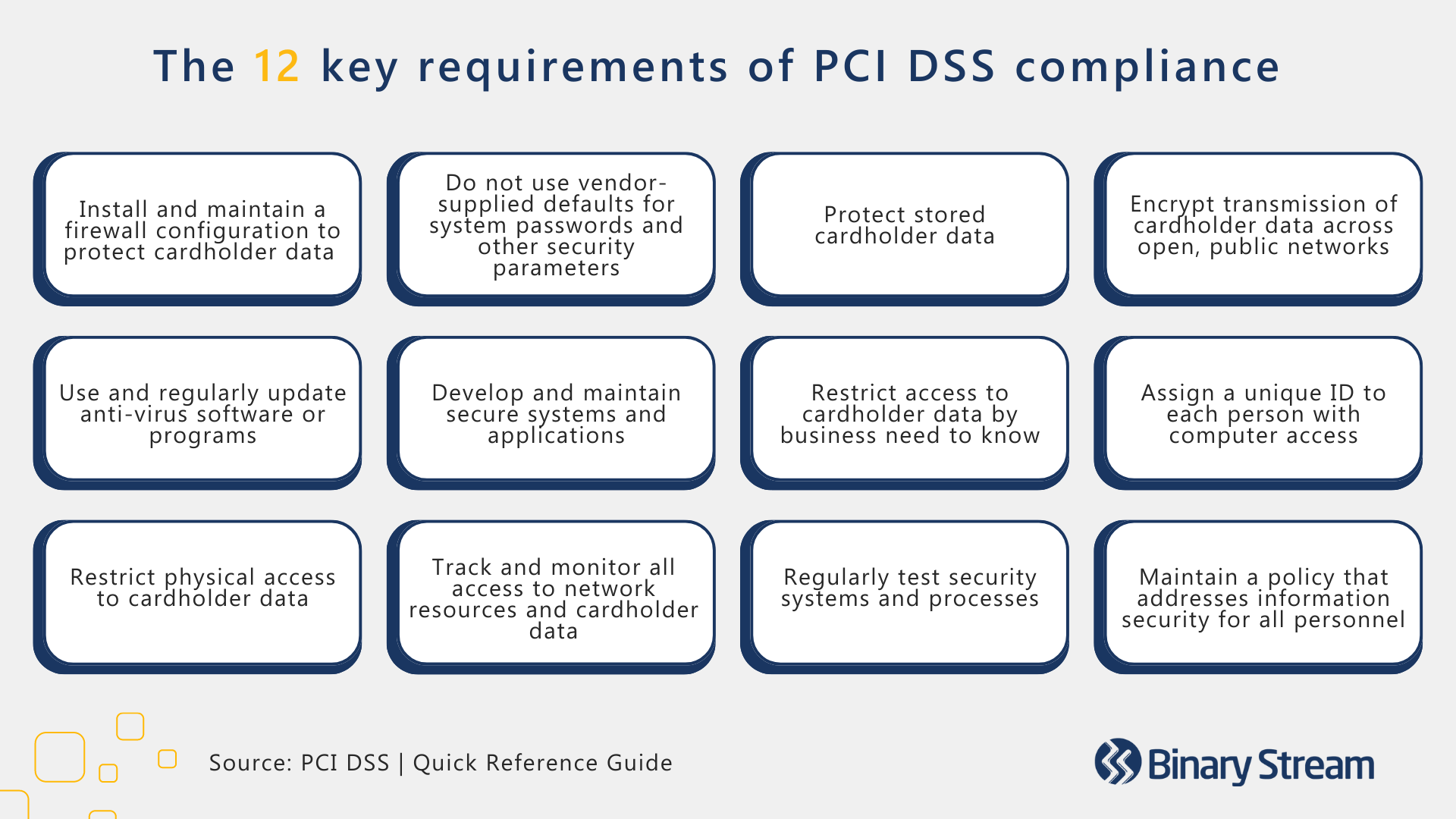
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of international standards advising businesses on best practices for processing payments securely. The volume of annual transactions your company achieves determines which level of compliance you must meet. The PCI DSS uses a four-level scale to classify businesses:
However, any company that accepts credit or debit card purchases must satisfy twelve essential requirements. While all products and services offered by PSPs must comply with the PCI DSS, understanding the basics will help to protect your company against fees and infractions.
There are many factors to consider when determining which payment gateway is the best fit for your business. While payment gateways tend to follow the same five-step approach, they each have limitations. Investing in software that meets all your business requirements is vital.
The following seven questions can help you narrow your search and define the hallmarks of a top-notch payment gateway:
1.) How many types of cards and payment methods does it support?
2.) Can it handle multiple currencies?
3.) Does it offer advanced security protocols, covering encryption and fraud protection?
4.) Is there clear and transparent communication around vendor fees?
5.) Does it integrate with your payment portal and e-commerce software?
6.) Is the front-end convenient and user-friendly?
7.) Will customers have access to 24/7 comprehensive customer support?
It depends. Using multiple payment gateways is more expensive and can muddle an otherwise clean UX, but there are some instances where it’s a beneficial strategy. Implementing more than one gateway expands customer payment options and allows you to assess whether one generates more conversions.
Finding one solution that meets all your business requirements and adequately addresses customer concerns can be tricky, especially for companies growing into international markets. Ultimately, you’ll likely need to experiment to determine the optimal arrangement for your business.
If you’re still feeling lost or are looking for more information, we’re here to help. Feel free to contact our experts with any lingering questions you may have. We can’t wait to meet you!
Many companies depend on payment processing companies to manage their online payments. However, completely relying on a third party can lead businesses to underestimate their payment gateway security risks and requirements, opening them up to data breaches and cybercrime. This issue only becomes magnified when companies undergo changes like expanding operations or migrating to a subscription billing model.
A study by PWC, Global Economic Crime and Fraud Survey 2022, found that 52% of companies with global annual revenues exceeding $10 billion experienced fraud in the past 24 months, with 18% losing over $50 million in their most disruptive incident. Among smaller companies earning less than $100 million annually, 38% experienced fraud; of those affected, 22% faced a total impact of over $1 million.
Therefore, online payment security must be a top priority to safeguard your business. Keep reading to discover five payment gateway security features every business needs to process transactions securely.
A payment gateway is an e-commerce merchant service that collects customers’ payment information to authorize a transaction, ensuring that the payment is legitimate. Payment gateways read, encrypt, and transmit data between the merchant’s website, the customer’s financial institution, and the merchant’s financial institution.
Further reading: Online payment gateways bring these 5 benefits
Payment gateway security is vital to guarding your customers’ personal data and protecting your company. Security breaches, fraud, and compliance violations are all costly mistakes that not only sacrifice your hard-earned revenue but jeopardize your brand’s reputation.
Under the European Union General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), breach or theft of cardholder data can result in penalties of up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is greater.
Additionally, payment providers can fine companies who breach the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) $5,000–$100,000 per month for non-compliance.
Therefore, as more customers embrace e-commerce for their purchasing needs, companies must be ready to provide a secure shopping experience.
Continuous learning is foundational to creating a culture of data security, so it’s critical that your team remain updated on the latest safety strategies and regularly evaluate whether it’s time for an upgrade. Below you’ll find five payment gateway security features that are necessary in today’s business climate.
Any company that processes credit or debit card purchases must comply with the international rules and regulations stated in the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). The main role of the PCI DSS is to provide businesses with a standardized approach to rigorous, secure transaction processes while retaining a smooth customer experience.
Maintaining PCI compliance is essential to avoiding penalties and improves your reputation with payment brands, builds customer trust, and bolsters your systems to prevent data breaches and credit card fraud. The PCI DSS has 12 key requirements, further broken down into 78 base requirements and 400 test procedures. The 12 key requirements are outlined in the image below:

Companies must adhere to different compliance levels based on their size. The PCI classifies businesses on a four-level scale by the number of transactions they process per year:
All legitimate processing providers are required to offer PCI-compliant services; however, it’s still worth investigating the PCI DSS as your business will be on the line for any non-compliance. When determining which payment processor to invest in, make sure it can manage credit card processing, transaction history, and credit card data management while complying with the PCI DSS.
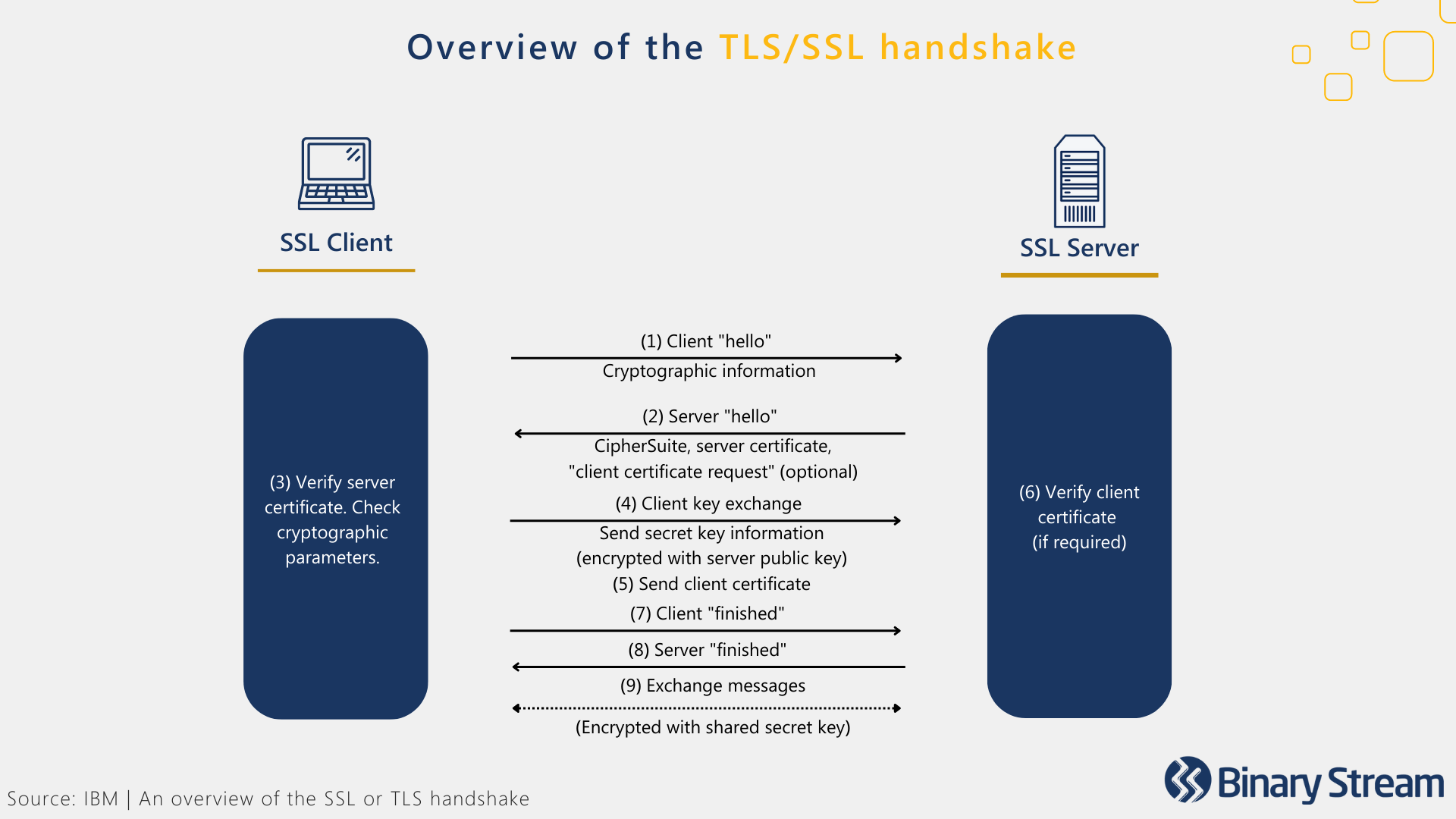
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols encrypt the online connection between the browser and the server, creating end-to-end protection for sensitive information. These security measures ensure the secure transmission of customer data collected by a payment gateway.
Here’s an overview of how the encryption process, nicknamed the “TLS/SSL handshake,” works:
If you’ve ever visited a website where the URL begins with HTTPS or has a padlock symbol next to it, then you’ve encountered TLS/SSL encryption. These hallmarks signify that the website is TLS/SSL certified and that your customers can trust your company with their payment information.
3D Secure (3-domain structure) or payer authentication, is a security feature that addresses issues of fraud in online debit or credit card transactions. Customers are required to complete an extra step of verification with their card issuer at checkout, engaging all three domains of payer authentication:
The most recent iteration, 3D Secure 2, allows for different methods of verification other than a password, including:
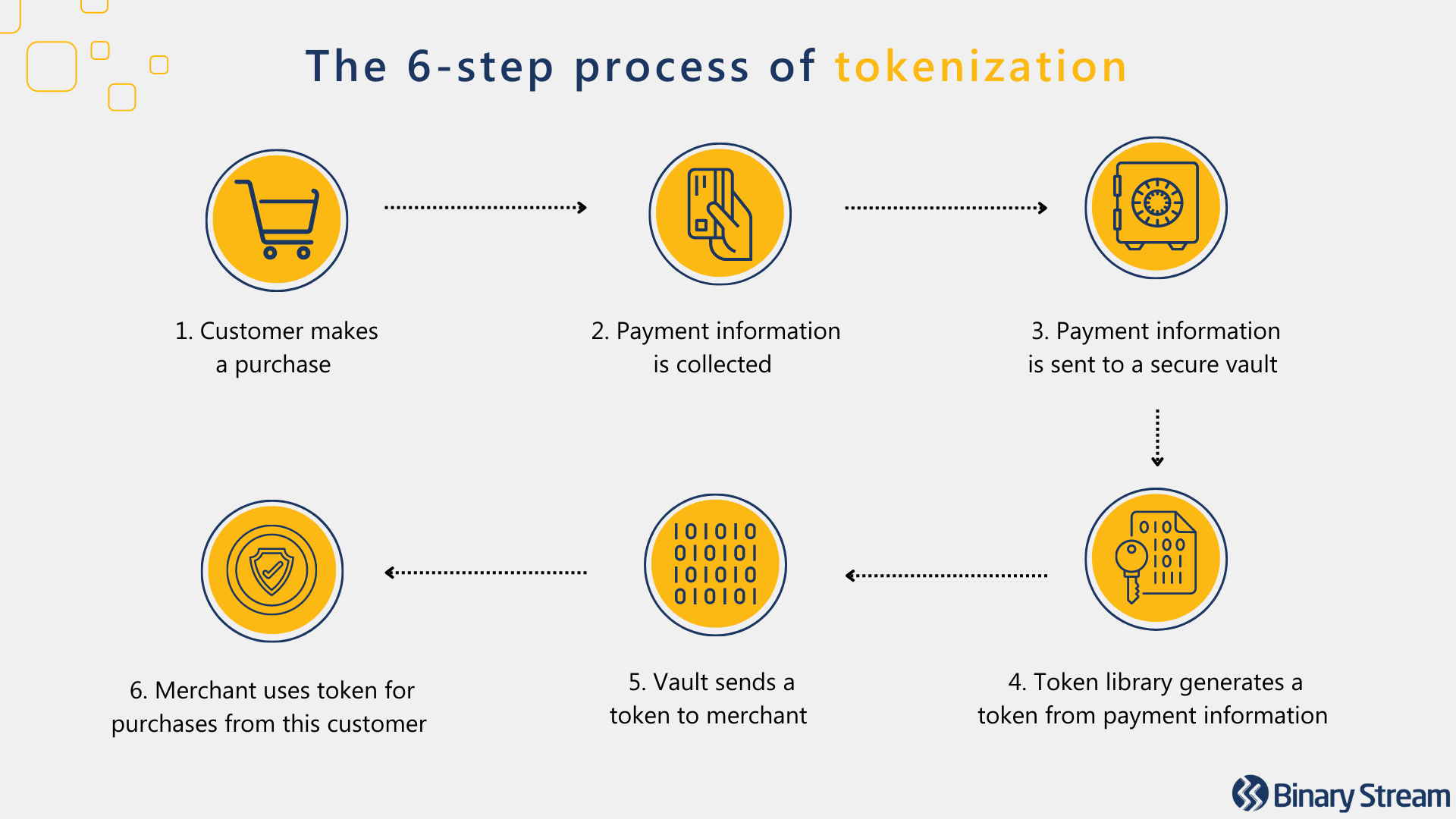
Tokenization secures customer payment details by replacing sensitive data with a string of randomly generated numbers, referred to as a ‘token.’ The PCI DSS promotes the adoption of payment tokenization with good reason.
Tokens provide one-to-one replacements for primary account numbers kept outside the merchant’s server. The merchant does not need to be responsible for storing sensitive information, protecting the merchant and customer against fraudulent activity.
This extra layer of protection renders confidential information meaningless and useless in a breach. If a hacker were to gain access to the tokens, their efforts would be wasted because they would have no way to decrypt them.
The address verification service (AVS) is another commonly used method to prevent credit card fraud. After a customer enters their billing address, AVS will check if it matches the one on file with the credit card provider. If it’s a match, then the transaction will be approved.
AVS can be an effective protocol for minimizing chargebacks. Verifying details about the cardholder provided during the purchasing process can help flag suspicious transactions and protect the company before fraud occurs.
Further reading: The ultimate checklist for the best recurring billing payment gateways